Indexes#
Querona allows defining an index on a View if the underlying database engine supports indexes. Managing indexes in Querona is available through GUI and SQL statements like CREATE INDEX and DROP INDEX.
Indexes in Querona are virtual, which means they have no representation in the underlying data store until a view is materialized.
Note
The underlying Querona provider has to support indexes, e.g., MS SQL Server, Azure SQL or Oracle. See Materialization for more details.
Managing indexes#
To manage indexes for a view navigate to .
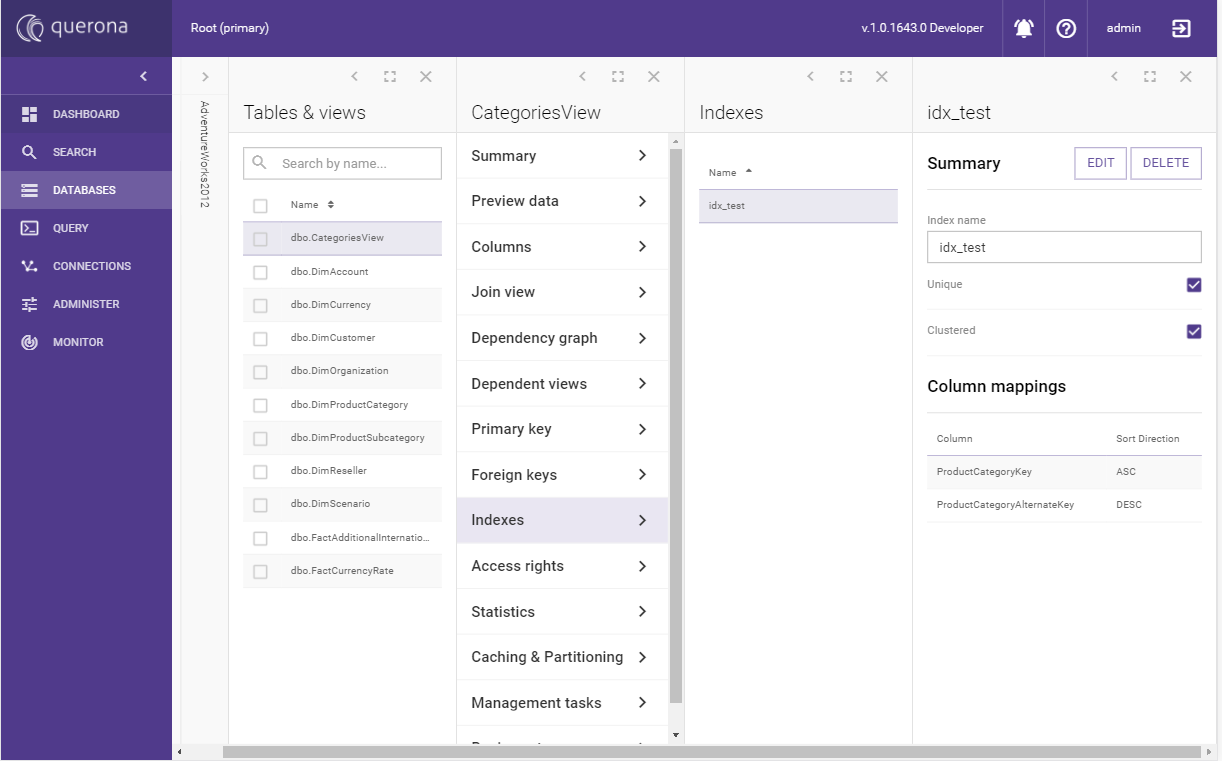
To add a new index, click the Add index button:
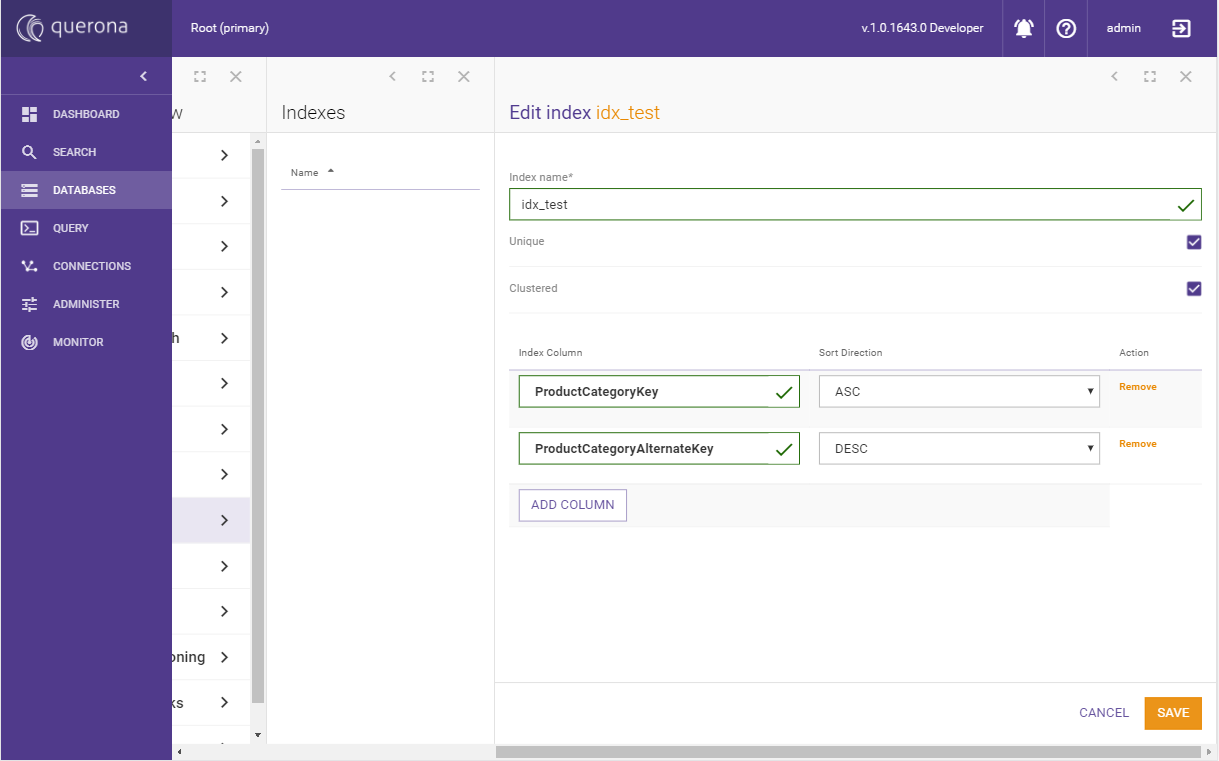
Enter the name of the index and select at least one column as an index member. Additional columns can be added using the Add column button.
Check the Unique, Clustered, or Columnar checkboxes if required.
Clicking Save will return you to the index list, displaying the newly created index in preview mode. If the Save button is disabled, the selected configuration is not supported. For example, clustered columnar indexes do not support included columns.
To remove an index, select it, then click Delete and confirm the action.
Physical index handling#
The handling of indexes varies depending on the underlying DBMS utilized in the virtual database. Feature availability in cloud-based DBMSs may be contingent on the selected tier, edition, or configuration. Querona leverages all supported features available within the underlying system and, when a desired feature is not supported, it will either adapt by selecting the closest alternative in terms of functionality and purpose or omit the feature if no suitable substitute exists.
For instance, assuming the underlying DBMS is Azure SQL, if materialized view includes both a Primary Key constraint and a clustered columnstore index, Querona will first create the columnstore index and convert the Primary Key constraint into a unique index. This adaptation is necessary because the desired combination is not supported on Azure SQL.
